Uncovering the Physics of Star-Forming Regions: A High-Resolution Study of Ionised Gas in M33
Contact Information
Description
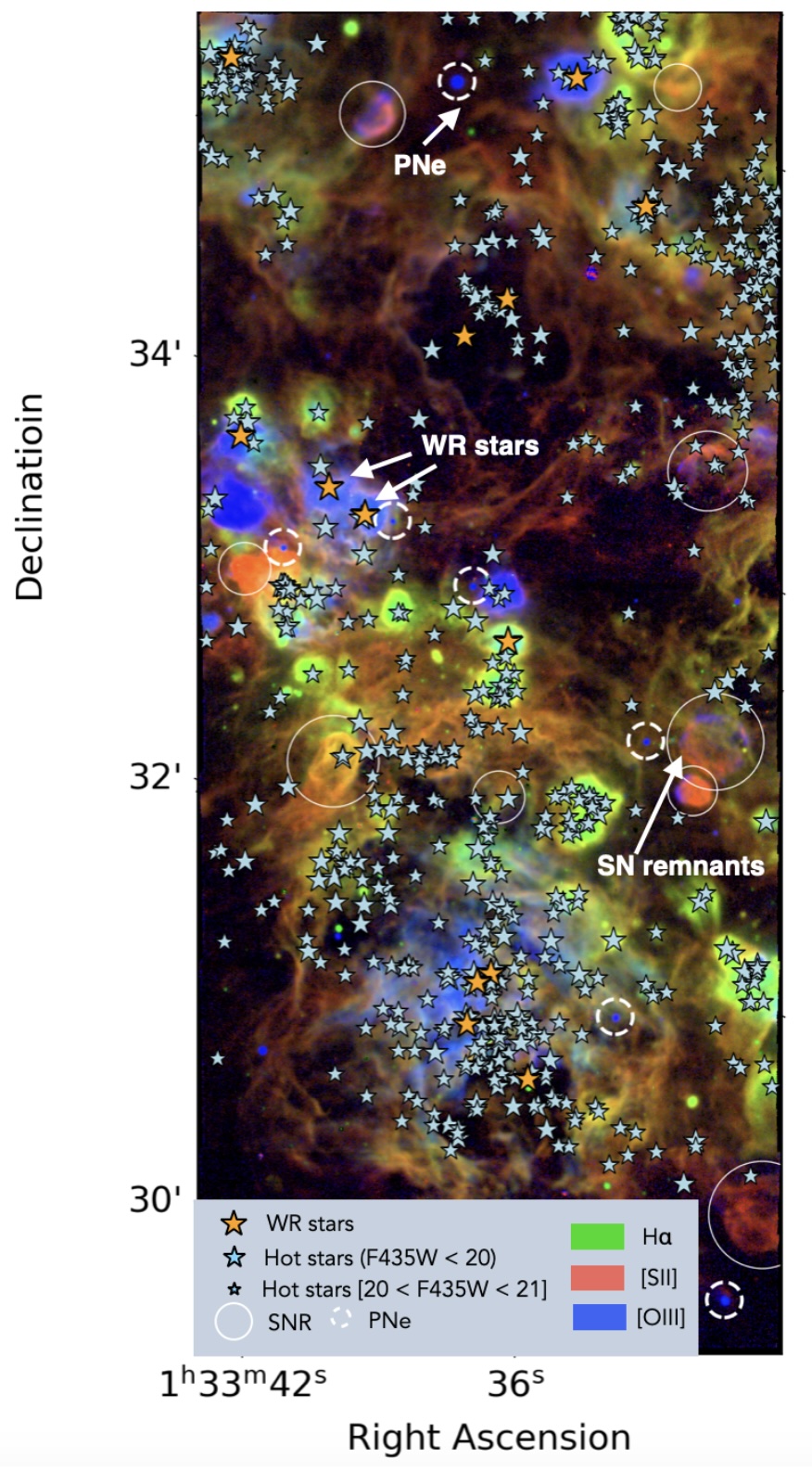
Star-forming regions in galaxies, known as H II regions, are clouds of gas ionised by young, massive stars. Studying their emission is essential to understand how galaxies form new stars and how these affect their surroundings. Significant progress in this field is now possible thanks to high-resolution VLT/MUSE integral field spectroscopic observations of the nearby galaxy M33, which provide exceptionally sharp maps of ionised gas at only a few parsecs resolution. MUSE provides in each pointing a data cube including the spectrum in each pixel (0.2”x0.2”) of the field of view of 1’x1’. Our M33 dataset is covering a mosaic of 24 MUSE pointings, for a total of 24 sq. arcmin and more than 2 million spectra.
The thesis project is focused on the analysis of this dataset which opens the way to several scientific investigations, including the characterisation of the internal structure of ionised nebulae, and the separation of compact H II regions from the more extended diffuse ionised gas (DIG). The main excitation source of this diffuse emission, as well as the physical differences and separation criteria from HII regions are still debated, and the sensitivity and spatial resolution of the MUSE data represent the best dataset for such investigation.
By combining the MUSE data with observations from HST, JWST, and ALMA, as well as with state-of-the-art photoionisation models, the project will explore which types of stars and physical processes are responsible for heating and ionising the gas in M33. The final goal is to build a detailed and reliable picture of how star formation and stellar feedback operate on small scales in a nearby spiral galaxy. Depending on interest, the thesis can focus on one or more of these scientific directions.
The student will have full access to the MUSE dataset (PI status), to analysis tools for spectral measurements, and to financial support for conference participation. Moreover, he/she will have the possibility of taking part in an observing run at the Very Large Telescope on Cerro Paranal in Chile, either for the ERIS or MOONS Guaranteed Time observing runs.
References
https://ui.adsabs.harvard.edu/abs/2025A%26A...697A.148B/abstract